The Technology section is published with the support of Favbet Tech


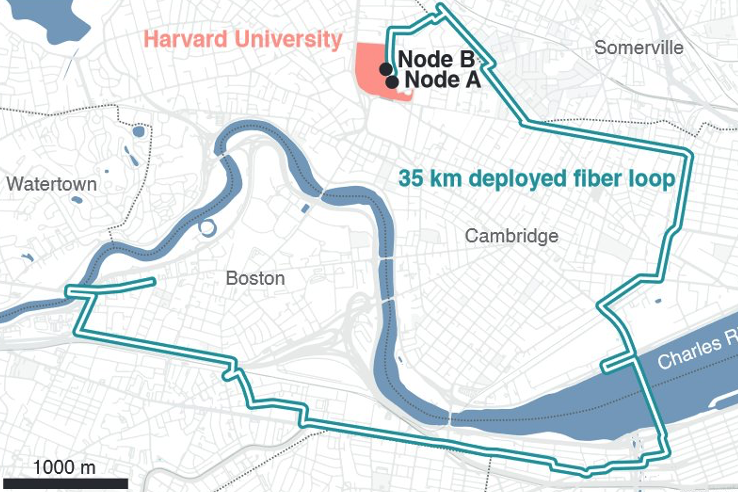
Amazon and Harvard University created a “quantum network” that transmitted an entangled photon from one quantum computer to another via 35 kilometers of fiber optic cable.
Researchers placed a set of nodes around Boston to build a network capable of “efficiently capturing, storing, and transmitting information that was originally stored in light.” Much like the Internet as we know it, quantum networks transmit information carried by light—in this case, quantum entangled photons. But they need “relays” to prevent photons from scattering over long distances, as light typically does. Repeaters must be able to send a photon without breaking its entanglement or changing the information.
Harvard and Amazon's AWS Center say that the experimental nodes use cavities in diamonds that “trap light and force it to interact with quantum memory.” These assemblies can be mass produced using existing technologies. During the experiments, the team took a qubit encoded into a photon and bounced it off a quantum memory in a Harvard lab.
“When a photon interacts with a quantum memory, it will become entangled in the memory — this means that measurements made on either the photon or the memory will provide information and thus change the state of each other.
However, instead of measuring the photon (that is, obtaining information), the photon undergoes a quantum conversion from the visible frequency (at which quantum memory operates) to the telecommunications frequency (where losses in the optical fiber are minimized). Thus the photon travels back and forth through an underground fiber optic network before returning to Harvard, where it reverts to visible frequency.
After completing this journey, the photon is reflected from another quantum memory in another laboratory, thus transferring the entanglement of the photon into this second memory. Finally, the photon bounces off the second memory and travels to a detector, which notices the photon's presence but does not reveal any of the underlying quantum information contained in the light. He is entangled with the memory – meaning that the measurements of either the photon or the memory change the state of each other. The photon is then converted from a visible frequency to a telecommunications frequency, which then bounces off to another laboratory, thus completing the journey.”
The first experiments showed that a quantum entangled photon traveled more than 35 kilometers. The entangled photon persisted for more than a second, which the company says is enough time for the light to travel more than 300,000 km and more than enough time to circle the world 7.5 times.
Quantum networks use the same principles as quantum computing, using the quantum state of photons to transfer information. Experiments with quantum networks have been going on for some time, but no one has yet created a fully commercial version. Scientists say many more improvements are needed before a quantum network becomes scalable and commercially viable. It's still slow and can only send one qubit at a time.
QA Manual Course (PZ manual testing) from Powercode academy. Learn how to find solutions and control the content of websites and add-ons. Sign up for a course


Favbet Tech is IT a company with 100% Ukrainian DNA, which creates perfect services for iGaming and Betting using advanced technologies and provides access to them. Favbet Tech develops innovative software through a complex multi-component platform that can withstand enormous loads and create a unique experience for players. The IT company is part of the FAVBET group of companies.