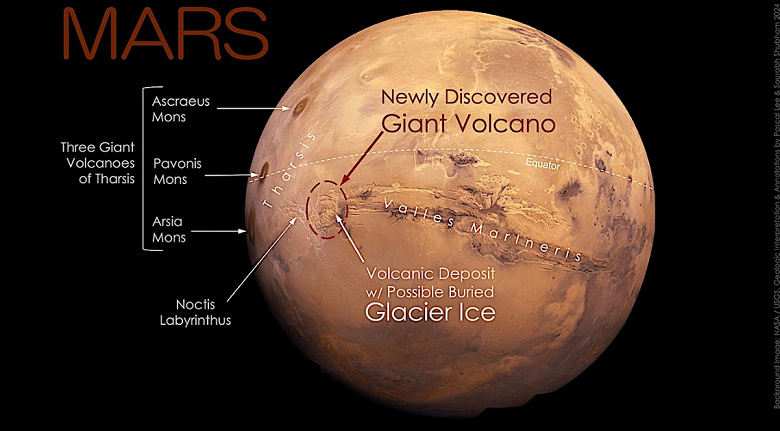
“Vulcan Noctis” opens up new prospects for research and searches for signs of past life on Mars
At the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC), held in The Woodlands, Texas, scientists reported the discovery of a giant volcano on Mars and a possible layer of glacial ice in the eastern part of the Martian volcanic province of Tharsis ( Tharsis), near the planet's equator.
A giant volcano that has repeatedly appeared in images of orbiting spacecraft, starting with Mariner 9. in 1971, but destroyed beyond recognition, hid in plain sight for decades in one of the most famous regions of Mars — on the border between the highly fragmented Labyrinth of Night (Noctis Labyrinthus) and the Valles Marineris canyon system.
This structure, temporarily named Volcano Noctis, turned out to be an impressive formation measuring 9022 meters in height and 450 kilometers in width. With a long history of geological changes, this volcano represents an interesting field of study for scientists and astronomers. The volcano's gigantic size and complex history of changes indicate that it has been active for a very long time. In its southeastern part there are thin layers of volcanic sediment, under which glacial ice is hidden. This opens up new possibilities for studying the geological evolution of Mars and searching for signs of past life.
«We studied the geology of the area where last year we found the remains of a glacier, and realized that we were inside a huge and deeply destroyed volcano», — said Dr. Pascal Lee, a planetary scientist at the SETI Institute and the Mars Institute and lead author of the study.
Numerous signs point to the volcanic nature of this area. For example, the structure's interior features arc-shaped elevations, and the gently sloping outer slopes extend for 225 kilometers. The ruins of a volcanic crater that was once filled with a lava lake are visible near the center of the structure. In addition, lava deposits, pyroclastic deposits (composed of volcanic particles such as ash, ash, and pumice) and hydrated minerals are found in several areas around the volcano.
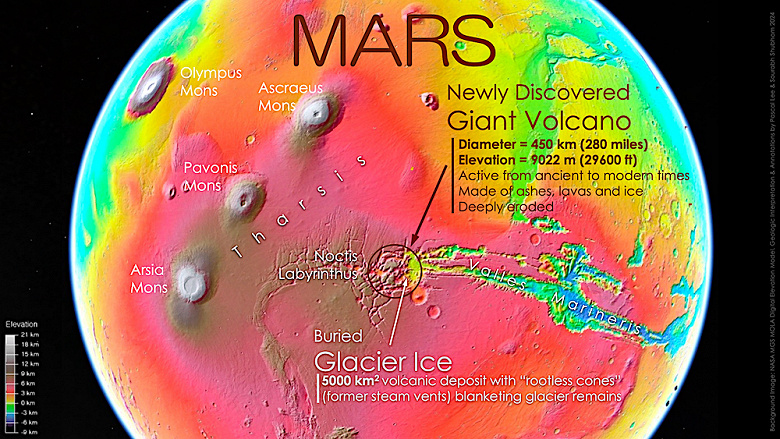
Scientists also discovered a large area of volcanic deposits extending over 5,000 square kilometers around the volcano. These deposits are low, rounded and elongated hills. They are thought to be the result of steam emission or steam swelling when hot volcanic material collides with water or ice crust at the surface.
Just a year ago, Lee and co-authors Sourabh Shubham and John Shutt discovered the remains of a relict glacier in an erosional vent in the same volcanic nappe as a light-colored sulfate salt deposit with the morphological features of a glacier. It was interpreted that sulfate deposits, consisting primarily of jarosite, a hydrous sulfate, formed when a sheet of volcanic pyroclastic materials came to rest on a glacier and reacted chemically with the ice. The eroded cones identified in the current study show similar occurrences of polyhydrate sulfates, further suggesting that the volcanic cover may conceal an extensive layer of glacial ice.
«Vulcan Noctis» has a long and complex history of change that is likely related to thermal and glacial erosion. Scientists view the volcano as a huge shield composed of layered deposits of pyroclastic materials, lava and ice, the latter accumulated as a result of repeated snowfall and glacial activity on its slopes. As cracks and fissures developed, particularly as the Tharsis region where the volcano is located rose up, lava began to penetrate various parts of the volcano, resulting in thermal erosion and the removal of much of the buried ice, as well as the collapse of parts of the volcano.
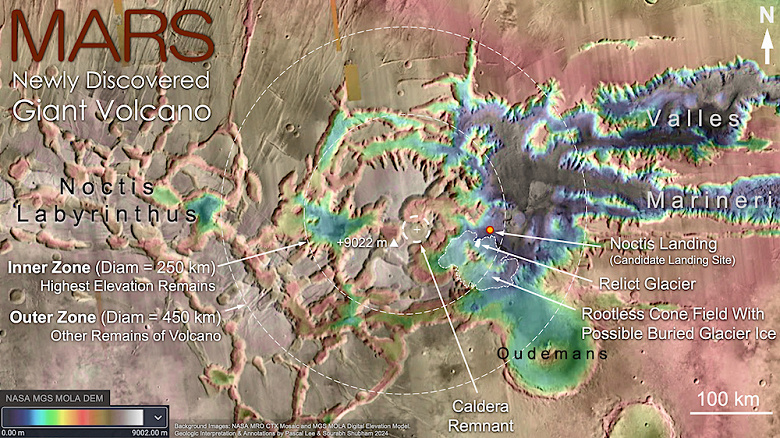
Subsequent glacial processes continued erosion and gave the canyons inside the volcano their current characteristic shape. In this context, «relict glacier» and a possible buried layer of glacial ice around the volcano may be remnants of the last episode of glaciation.
But much about this newly discovered giant volcano remains a mystery. Although it is known to have been active for a long time and began to form in the early history of Mars, there is no exact time frame for its formation. Likewise, although eruptions have been recorded, it is unknown whether it remains active and is likely to erupt again. If «Volcano Noctis» been active for a very long time, it is possible that the combination of constant heat and access to water from the underlying ice layer could have made this a favorable location for the development of life.
As the mysteries surrounding the volcano continue to preoccupy scientists, the region is becoming increasingly attractive for studying the geological evolution of Mars, searching for signs of past life and planning future missions using robots and perhaps a future target for astronaut exploration. Currently, the presence of glacial ice near the equator gives hope that in warmer areas of the planet it will be possible to extract water for hydration and the production of rocket fuel.
«A combination of factors makes “Volcano Noctis” an extremely interesting place. This ancient and long-lived volcano is so destroyed that its structures can be explored on foot, by rovers or by drones to explore its different parts, take samples and date it, exploring its evolution over time. It has a long history of interacting with heat, water and ice, making it an ideal location for astrobiology and the search for signs of life. Finally, the presence of glacial ice at shallow depths near the planet's equator makes this location very attractive for robotic and human exploration», — Lee emphasized.